AI in European Industry: How Artificial Intelligence Shapes New Roles for Managers and Specialists (Competencies 2026)
2025-10-27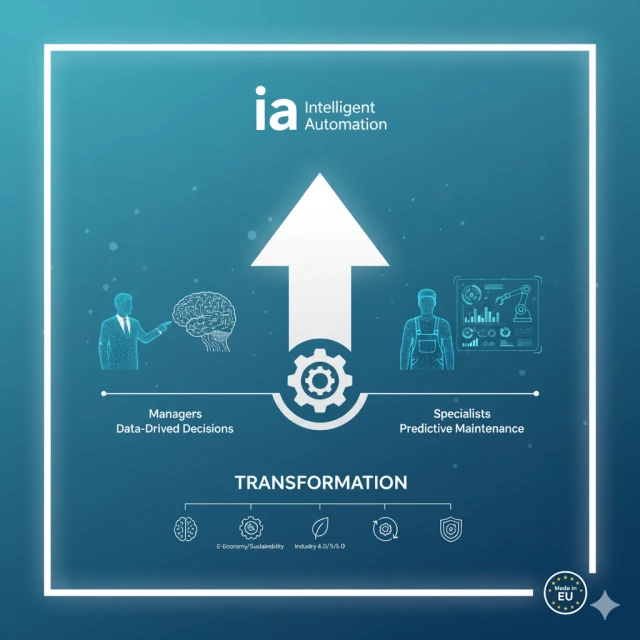
1. Evolution of Work: From Industry 4.0 to Competencies 5.0
Across Europe, from the Old Continent to Scandinavia, industry faces the dual challenge of a shortage of skilled workers and a growing need for sustainable and efficient production. AI is not viewed as a threat but as a crucial tool to address these issues. The European strategy emphasizes Industry 5.0, where technology is intended to support employee well-being, not just efficiency.
-
Paradigm Shift: AI and robotics are taking over tasks requiring precision and repeatability, freeing up employees for creative and analytical roles.
2. Managers: Data-Driven Strategic Decisions
The role of management in a European factory is undergoing a fundamental change. Instead of supervising every process, managers are becoming architects and interpreters of data.
-
New Managerial Responsibilities:
-
AI-Powered Decision Making: Utilizing AI models for demand forecasting, supply chain risk management, and resource optimization (including energy).
-
Digital Twin Implementation: Employing virtual factory models to simulate changes and investments before they are physically implemented.
-
Cultural Change Management: Guiding teams through digital transformation processes, focusing on reskilling to retain experienced employees amidst technological shifts.
-
-
Key Competency: Business AI literacy and the ability to integrate AI into strategic company goals (e.g., ESG – Environmental, Social, and Governance).
3. Maintenance Specialists: Precision and Proactivity
The role of Maintenance, Repair, and Operations (MRO) technicians and engineers is experiencing the most visible metamorphosis. Thanks to IoT (Internet of Things) and AI, they are transitioning from reactive firefighting to predictive management.
-
Maintenance Revolution:
-
Predictive Diagnostics (PdM): AI systems monitor thousands of data points from machines in real-time, identifying subtle signs of wear. The employee intervenes not at the point of failure, but based on algorithmic recommendations.
-
IT/OT Integration: Specialists must be adept at navigating both operational technology (machines, controllers) and information technology (networks, cloud, databases).
-
Virtual Support: Utilizing Augmented Reality (AR) technology, such as specialized goggles, for remote diagnostics and repairs with expert assistance.
-
-
Key Competency: Knowledge of Condition Monitoring methods, cybersecurity in an industrial environment, and the ability to work with cloud-based systems.
4. New Specializations: Experts in the E-Economy
Driven by the European Green Deal and the increasing importance of data, new highly valued roles are emerging in the European market:
-
Industrial Data Scientist: Responsible for building and validating AI models that optimize material consumption and minimize waste – crucial for the Circular Economy.
-
AI-Powered Energy Efficiency Expert: A specialist focused on using AI to optimize utility consumption, including managing proprietary RES (Renewable Energy Sources) installations (e.g., energy storage and photovoltaics) to reduce costs and meet regulatory requirements.
5. Conclusion: Investing in Digital Human Capital
The future of European competitiveness depends on the synergy of advanced technologies and a competent workforce. Investments in digitalization must go hand-in-hand with investments in people. Companies that offer effective upskilling and reskilling programs will be the leaders of European industry in 2026.
Content added:
 Marcin Białczyk
Marcin Białczyk



 使用以下方式登录 Facebook
使用以下方式登录 Facebook 使用以下方式登录 Google
使用以下方式登录 Google